What is a Roller Thrust Bearing?
Roller thrust bearings are specialized mechanical components designed to handle axial loads in rotating machinery. These bearings consist of cylindrical or tapered rollers positioned between two rings, allowing for smooth rotation while supporting significant thrust forces. Commonly used in various industrial applications, roller thrust bearings play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and longevity of equipment that experiences axial loads during operation.
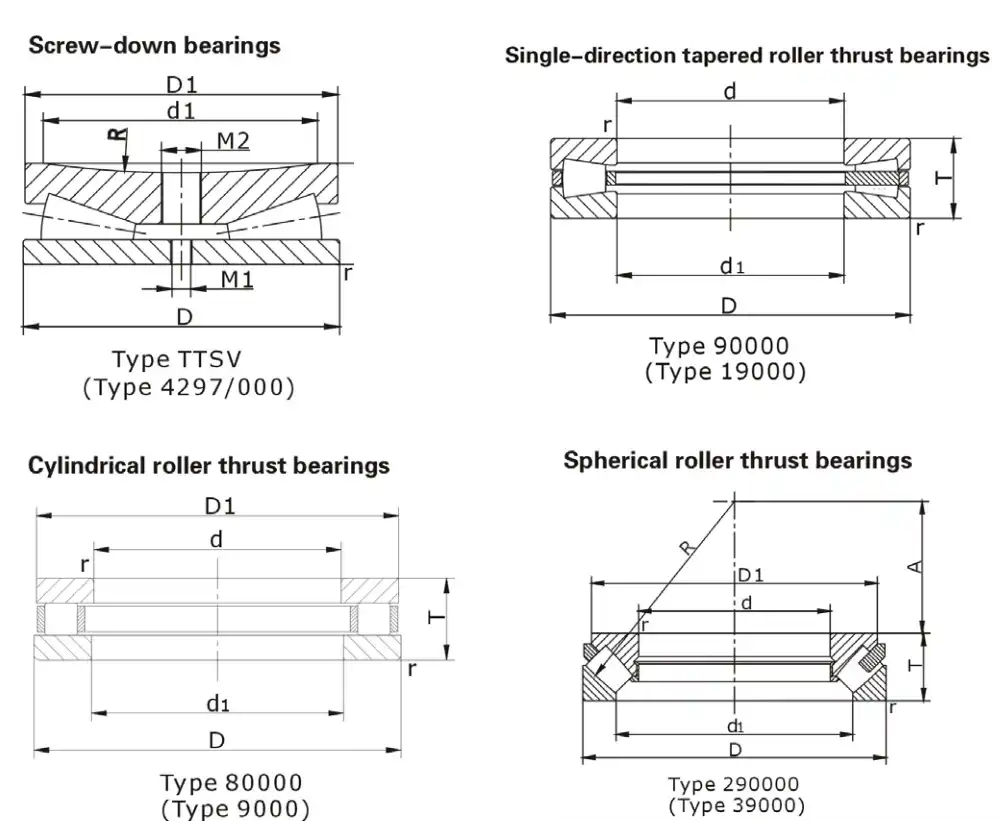
How do roller thrust bearings differ from other types of bearings?
Roller thrust bearings stand out from other bearing types due to their unique design and specific load-handling capabilities. Unlike radial bearings that primarily manage forces perpendicular to the shaft, roller thrust bearings are engineered to handle axial loads, which are forces parallel to the shaft axis. This specialization makes them indispensable in applications where axial forces are predominant.
The key differences between roller thrust bearings and other bearing types lie in their construction and load-bearing capacity. While ball thrust bearings also handle axial loads, roller thrust bearings offer superior load-carrying capacity due to their larger contact area between the rolling elements and the raceways. This increased surface area allows for better distribution of forces, resulting in reduced stress on individual components and improved overall performance.
Compared to radial bearings, roller thrust bearings have a more compact axial profile, making them ideal for applications where space is limited along the shaft axis. Their design allows for higher axial load capacities in a smaller package, which is particularly advantageous in heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
Another distinguishing feature of roller thrust bearings is their ability to accommodate misalignment to a certain degree. This flexibility makes them suitable for applications where slight shaft deflections or housing misalignments may occur, enhancing their versatility across various industrial settings.
What are the main applications of thrust roller bearings?
Thrust roller bearings find widespread use across numerous industries due to their exceptional ability to handle heavy axial loads while facilitating smooth rotational movement. Their versatility and reliability make them essential components in a wide range of machinery and equipment.
In the automotive industry, thrust roller bearings play a critical role in transmission systems, particularly in automatic transmissions. They support the thrust loads generated by helical gears and ensure smooth operation of the gearbox. These bearings are also commonly found in steering columns, where they facilitate the smooth rotation of the steering wheel while handling the axial forces exerted during steering maneuvers.
The aerospace sector relies heavily on thrust roller bearings in various applications. They are used in aircraft engines, specifically in the thrust reversers, which redirect engine exhaust to provide deceleration during landing. Thrust roller bearings are also essential in helicopter rotor systems, where they support the immense axial loads generated by the main rotor while allowing for smooth rotation.
In the field of heavy machinery and construction equipment, thrust roller bearings are indispensable. They are used in excavators, bulldozers, and cranes to support the axial loads in swing bearings and slewing rings. These bearings enable the smooth rotation of large structures while handling the substantial thrust forces generated during operation.
The marine industry utilizes thrust roller bearings in propulsion systems, particularly in large ships. These bearings support the immense axial loads produced by propellers, ensuring efficient power transmission and smooth operation of the propulsion shaft.
In industrial manufacturing, thrust roller bearings are crucial components in machine tools such as lathes, milling machines, and grinding machines. They support the axial loads generated during cutting operations, maintaining precision and stability in the machining process.
The oil and gas industry relies on thrust roller bearings in various applications, including drilling equipment, pumps, and compressors. These bearings handle the high axial loads encountered in deep-well drilling operations and ensure the reliable operation of critical equipment in harsh environments.
How to properly maintain and lubricate thrust roller bearings?
Proper maintenance and lubrication of thrust roller bearings are essential for ensuring their optimal performance and longevity. A well-maintained bearing can significantly extend the operational life of machinery and reduce the risk of unexpected failures.
The first step in maintaining thrust roller bearings is to establish a regular inspection schedule. This involves visually examining the bearings for signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Look for any discoloration, pitting, or scoring on the rolling elements and raceways. Additionally, check for any unusual noises, vibrations, or excessive heat generation during operation, as these can be indicators of potential bearing issues.
Cleanliness is paramount in bearing maintenance. Ensure that the environment around the bearing is kept free from dust, debris, and moisture. Use appropriate seals and shields to prevent contaminants from entering the bearing assembly. If disassembly is required for cleaning, use clean, lint-free cloths and appropriate solvents to remove any old grease or debris. Be sure to handle the bearings with care to avoid introducing new contaminants or causing damage.
Lubrication is a critical aspect of thrust roller bearing maintenance. The choice of lubricant depends on factors such as operating conditions, speed, load, and temperature. In general, greases are preferred for thrust roller bearings due to their ability to stay in place and provide a protective barrier against contaminants. However, in high-speed applications or where heat dissipation is crucial, oil lubrication may be more appropriate.
When applying grease, it's essential to use the correct amount. Over-greasing can lead to increased operating temperatures and reduced efficiency, while under-greasing can result in inadequate lubrication and premature wear. Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for grease quantity and relubrication intervals. In many cases, a general guideline is to fill the bearing to about 30-50% of its free space with grease.
For oil-lubricated thrust roller bearings, maintain the proper oil level and ensure that the oil is clean and free from contaminants. Regular oil analysis can help detect any signs of bearing wear or oil degradation, allowing for timely interventions.
Proper alignment is crucial for the longevity of thrust roller bearings. Misalignment can lead to uneven load distribution, increased wear, and premature failure. Use appropriate alignment tools and techniques to ensure that the bearing is correctly positioned relative to the shaft and housing.
Temperature monitoring is an effective way to detect potential bearing issues. Unusually high operating temperatures can indicate problems such as inadequate lubrication, overloading, or misalignment. Implement temperature monitoring systems or perform regular temperature checks using infrared thermometers to identify any abnormal temperature increases.
In applications where thrust roller bearings are subjected to heavy loads or operate in critical equipment, consider implementing condition monitoring techniques such as vibration analysis. These advanced monitoring methods can provide early warning of developing bearing issues, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
When replacing thrust roller bearings, always use high-quality components that meet or exceed the original specifications. Improper bearing selection or the use of substandard parts can lead to premature failure and potential equipment damage.
By following these maintenance and lubrication practices, you can significantly extend the service life of thrust roller bearings, improve equipment reliability, and reduce overall maintenance costs.
Luoyang Huigong Bearing Technology Co., Ltd. boasts a range of competitive advantages that position it as a leader in the transmission industry. Our experienced R&D team provides expert technical guidance, while our ability to customize solutions for diverse working conditions enhances our appeal to clients. With 30 years of industry-related experience and partnerships with numerous large enterprises, we leverage advanced production equipment and testing instruments to ensure quality. Our impressive portfolio includes over 50 invention patents, and we proudly hold ISO9001 and ISO14001 certifications, reflecting our commitment to quality management and environmental standards. Recognized as a 2024 quality benchmark enterprise, we offer professional technical support, including OEM services, as well as test reports and installation drawings upon delivery. Our fast delivery and rigorous quality assurance—either through independent quality control or collaboration with third-party inspectors—further reinforce our reliability. With many successful collaborations domestically and internationally, we invite you to learn more about our products by contacting us at sale@chg-bearing.com or calling our hotline at +86-0379-65793878.
References:
1. SKF Group. (2021). Roller thrust bearings. SKF.com.
2. Timken Company. (2022). Thrust Bearings. Timken.com.
3. NSK Ltd. (2020). Thrust Roller Bearings. NSK.com.
4. Schaeffler Group. (2021). Axial cylindrical roller bearings. Schaeffler.com.
5. NTN Corporation. (2019). Thrust Roller Bearings. NTN.co.jp.
6. Machine Design. (2018). What's the Difference Between Thrust and Radial Bearings? MachineDesign.com.
7. Bearing Tips. (2020). Proper Lubrication of Roller Bearings. BearingTips.com.
8. Power Transmission Engineering. (2017). Thrust Bearing Basics. PowerTransmission.com.
9. Applied Industrial Technologies. (2021). Bearing Maintenance Best Practices. Applied.com.
10. Machinery Lubrication. (2019). Lubrication of Thrust Roller Bearings. MachineryLubrication.com.

