How is a Roller Slewing Bearing Different from a Ball Slewing Bearing?
Slewing bearings are critical components in numerous industrial and mechanical applications, serving as pivotal elements that enable rotation while supporting substantial loads. The distinction between roller and ball slewing bearings represents a nuanced yet crucial aspect of mechanical engineering, with each design offering unique advantages that can significantly impact machinery performance, efficiency, and longevity.
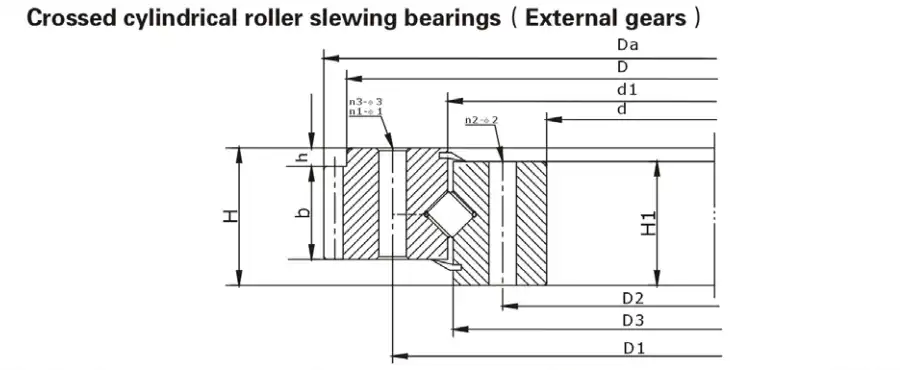
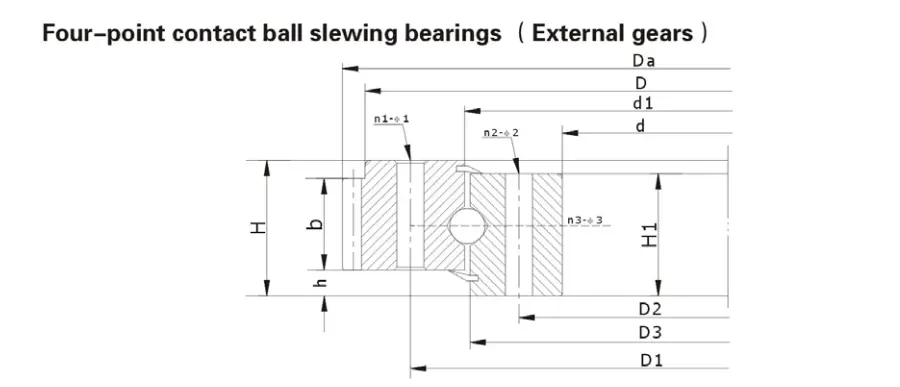
What Makes Roller Slewing Bearings Unique in Industrial Applications?
Roller slewing bearings stand out as sophisticated mechanical solutions designed to handle complex load distributions in heavy-duty industrial environments. Unlike traditional bearing designs, these specialized components incorporate cylindrical rollers arranged strategically to maximize load-bearing capabilities and minimize friction.
The fundamental architecture of roller slewing bearings revolves around their ability to distribute loads across multiple contact points. Each cylindrical roller acts as an independent load-bearing element, creating a more uniform stress distribution compared to alternative bearing types. This unique characteristic allows roller slewing bearings to excel in applications requiring exceptional load-carrying capacity, particularly in scenarios involving eccentric or asymmetrical loading conditions.
Engineers and designers appreciate roller slewing bearings for their remarkable versatility across diverse industrial sectors. In construction machinery like excavators and cranes, these bearings provide critical rotational support while managing extreme radial, axial, and moment loads simultaneously. The intricate design enables smooth, precise movement even under challenging environmental conditions, making them indispensable in demanding operational contexts.
The material selection for roller slewing bearings further enhances their performance capabilities. Typically manufactured using high-grade alloy steels with specialized heat treatments, these bearings demonstrate exceptional resistance to wear, fatigue, and environmental degradation. Manufacturers employ advanced metallurgical techniques to optimize the microstructure, ensuring superior hardness, toughness, and dimensional stability.
One notable advantage of roller slewing bearings lies in their ability to accommodate misalignment and slight geometric inconsistencies. The cylindrical roller configuration allows for more forgiving mounting requirements compared to more rigid bearing designs. This flexibility translates into reduced installation complexities and potentially lower overall system maintenance costs.
From wind turbine nacelles to massive mining equipment, roller slewing bearings prove their worth by providing reliable, high-performance rotational interfaces. Their capacity to handle substantial loads while maintaining minimal friction makes them a preferred choice in engineering applications demanding precision and durability.

How Do Ball Slewing Bearings Compare to Roller Designs in Heavy-Duty Machinery?
Ball slewing bearings represent an alternative approach to rotational load management, utilizing spherical ball elements to facilitate movement and load transfer. While sharing fundamental operational principles with roller designs, ball slewing bearings distinguish themselves through unique mechanical characteristics that render them suitable for specific industrial applications.
The primary differentiating factor in ball slewing bearings is the implementation of ball elements, which introduce distinct load distribution and friction dynamics. These spherical components enable lower friction coefficients compared to roller configurations, resulting in smoother rotational experiences and potentially reduced energy consumption in mechanical systems.
Precision emerges as a critical attribute of ball slewing bearings, particularly in applications requiring extremely tight tolerances and minimal play. Industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, robotics, and high-precision astronomical equipment frequently leverage ball slewing bearings to achieve exceptional positional accuracy. The controlled contact between ball elements ensures minimal deviation during rotational movements.
Structural complexity represents another fascinating aspect of ball slewing bearings. Manufacturers carefully design race configurations that optimize ball movement, implementing sophisticated geometric patterns that maximize load-bearing efficiency. Multiple race arrangements allow for enhanced load distribution, with some advanced designs incorporating separate races for radial, axial, and moment loads.
The thermal management capabilities of ball slewing bearings warrant particular attention. Their inherent design facilitates superior heat dissipation compared to some alternative bearing types, making them particularly valuable in high-temperature or thermally sensitive environments. The reduced contact area between ball elements and races contributes to more effective thermal regulation.
From a material science perspective, ball slewing bearings benefit from continuous technological innovations. Advanced ceramic coatings, precision-ground steel alloys, and innovative lubrication strategies have dramatically expanded their performance envelope. Modern ball slewing bearings can operate under extreme temperatures, corrosive environments, and challenging mechanical stress conditions.

Why Do Engineers Choose Specific Slewing Bearing Types for Different Projects?
The selection process for slewing bearings transcends simple mechanical considerations, encompassing a complex interplay of engineering requirements, operational constraints, and performance expectations. Engineers approach bearing selection through a holistic lens, evaluating multiple factors that influence overall system effectiveness.
Load characteristics emerge as a primary determinant in bearing selection. Roller slewing bearings excel in scenarios involving heavy, unevenly distributed loads, making them ideal for construction and mining equipment. Conversely, ball slewing bearings shine in precision-driven applications requiring minimal friction and exceptional positional control.
Environmental conditions play a significant role in bearing type selection. Factors such as temperature range, potential exposure to corrosive substances, and contamination risks directly impact bearing performance. Roller designs might prove more robust in harsh, debris-laden environments, while ball bearings could offer superior performance in clean, temperature-controlled settings.
Cost considerations cannot be overlooked during the selection process. While initial procurement expenses represent one aspect, engineers must evaluate long-term operational costs, including maintenance requirements, potential downtime, and replacement frequencies. Each bearing type presents unique economic implications that extend beyond immediate financial investments.
Technological advancements continue to blur traditional boundaries between roller and ball slewing bearing designs. Hybrid configurations and innovative material technologies are gradually emerging, promising enhanced performance characteristics that challenge conventional design paradigms.
Conclusion
The intricate world of slewing bearings reveals a fascinating landscape of mechanical engineering innovation. Both roller and ball designs offer unique advantages, demonstrating the remarkable complexity underlying seemingly simple rotational mechanisms.

Luoyang Huigong Bearing Technology Co., Ltd. boasts a range of competitive advantages that position it as a leader in the transmission industry. Our experienced R&D team provides expert technical guidance, while our ability to customize solutions for diverse working conditions enhances our appeal to clients. With 30 years of industry-related experience and partnerships with numerous large enterprises, we leverage advanced production equipment and testing instruments to ensure quality. Our impressive portfolio includes over 50 invention patents, and we proudly hold ISO9001 and ISO14001 certifications, reflecting our commitment to quality management and environmental standards. Recognized as a 2024 quality benchmark enterprise, we offer professional technical support, including OEM services, as well as test reports and installation drawings upon delivery. Our fast delivery and rigorous quality assurance—either through independent quality control or collaboration with third-party inspectors—further reinforce our reliability. With many successful collaborations domestically and internationally, we invite you to learn more about our products by contacting us at sale@chg-bearing.com or calling our hotline at +86-0379-65793878.
References
1. SKF Bearing Handbook, 2020 Edition
2. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering, "Advanced Bearing Technologies" (2019)
3. ASME Technical Paper on Precision Rotational Interfaces (2021)
4. Materials Science and Engineering Review, Volume 45, Issue 3
5. Industrial Machinery Design Quarterly, "Slewing Bearing Performance Analysis" (2022)
6. Mechanical Engineering International Conference Proceedings (2020)
7. Advanced Manufacturing Technologies Journal
8. Bearing Technology Innovations Research Report (2021)
9. International Standards Organization Bearing Design Guidelines
10. Mechanical Engineering Design Manual, 15th Edition

