What Are Angular Contact Ball Bearings Used In?
Angular contact ball bearings are specialized mechanical components designed to handle both radial and axial loads simultaneously. These versatile bearings find applications across various industries due to their unique design and capabilities. In this blog post, we'll explore the diverse uses of angular contact ball bearings and answer some common questions about their applications and characteristics.
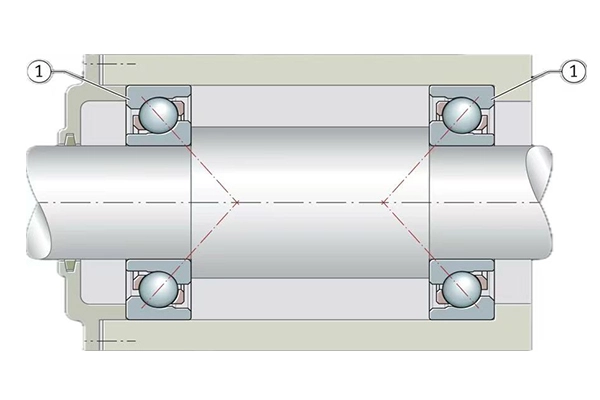
What are the advantages of angular contact ball bearings?
Angular contact ball bearings offer several advantages that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. One of their primary benefits is their ability to handle combined loads – both radial and axial – in a single bearing assembly. This capability is due to their unique design, which features raceways that are displaced relative to each other in the direction of the bearing axis.
The angled raceways allow for higher speed operation compared to other bearing types, making them ideal for high-speed applications. This design also enables angular contact ball bearings to maintain precision and accuracy even under heavy loads and high speeds. The contact angle between the balls and the raceways can be optimized for specific applications, providing flexibility in design and performance.
Another advantage of angular contact ball bearings is their ability to be preloaded. Preloading involves applying a controlled axial force to the bearing, which eliminates internal clearances and increases stiffness. This feature is particularly useful in applications that require high precision and rigidity, such as machine tool spindles and robotics.
Angular contact ball bearings also offer excellent runout control, which is crucial for maintaining accurate shaft positioning. This property makes them ideal for applications where precise rotational movement is essential, such as in medical equipment and optical devices.
Furthermore, these bearings have a relatively low friction coefficient, which contributes to reduced heat generation and improved energy efficiency. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in high-speed applications where heat buildup can be a significant concern.
The versatility of angular contact ball bearings extends to their mounting configurations. They can be used in single, double, or multiple-row arrangements, allowing for customization based on specific load and space requirements. This flexibility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries.
How do you install angular contact ball bearings?
Installing angular contact ball bearings correctly is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The installation process requires attention to detail and adherence to specific procedures to avoid damage and ensure proper functioning.
The first step in installing angular contact ball bearings is to carefully inspect the bearing and the housing or shaft where it will be mounted. Ensure that all components are clean and free from debris, as even small particles can affect the bearing's performance. It's also essential to check that the mounting surfaces are smooth and within the specified tolerances.
Before installation, it's crucial to determine the correct mounting arrangement. Angular contact ball bearings can be mounted in various configurations, including single, duplex (back-to-back or face-to-face), or tandem arrangements. The choice depends on the specific application requirements, such as load direction and magnitude.
When handling the bearing, it's important to use clean, lint-free gloves to prevent contamination. Never apply force directly to the rolling elements or cages during installation. Instead, use appropriate tools and techniques to apply force evenly to the bearing rings.
For shaft mounting, the inner ring of the bearing should be heated uniformly to expand it slightly, allowing for easy installation onto the shaft. This can be done using an induction heater or an oil bath. The temperature should be carefully controlled to avoid damaging the bearing. Once heated, the bearing should be quickly and accurately positioned on the shaft.
For housing mounting, the outer ring may need to be cooled using dry ice or liquid nitrogen to contract it slightly. This allows for easier insertion into the housing. Again, care must be taken to avoid temperature extremes that could damage the bearing.
When installing multiple bearings in a duplex or tandem arrangement, it's crucial to maintain the correct relative positions of the bearings. Many manufacturers provide matched sets with specific markings to ensure proper orientation.
Proper lubrication is essential during and after installation. The choice of lubricant depends on the application requirements, operating conditions, and manufacturer recommendations. It's important to use the correct amount of lubricant, as both under- and over-lubrication can lead to premature bearing failure.
After installation, it's important to check the bearing's runout and preload (if applicable). This ensures that the bearing is correctly seated and functioning as intended. Any discrepancies should be addressed before putting the equipment into service.
Finally, it's crucial to follow the manufacturer's recommendations for break-in procedures and initial operation. This may involve running the bearing at reduced speeds or loads for a specified period to allow for proper seating and distribution of lubricant.
What is the difference between deep groove and angular contact ball bearings?
Deep groove ball bearings and angular contact ball bearings are both widely used bearing types, but they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate bearing for a specific use case.
The most significant difference between these two bearing types lies in their geometry and load-carrying capabilities. Deep groove ball bearings have raceways that are deeply grooved and closely conform to the shape of the balls. This design allows them to support primarily radial loads, with some limited capacity for axial loads in both directions. The balls in a deep groove bearing make contact with the inner and outer races at a single point each, resulting in a contact angle close to zero.
In contrast, angular contact ball bearings have raceways that are displaced relative to each other in the direction of the bearing axis. This design creates a contact angle between the balls and the raceways, typically ranging from 15 to 40 degrees. This angled contact allows angular contact bearings to support combined radial and axial loads more effectively than deep groove bearings.
The load-carrying capacity is another key differentiator. Deep groove ball bearings excel at handling pure radial loads and can accommodate moderate axial loads in both directions. However, their capacity for axial loads is limited compared to angular contact bearings. Angular contact bearings, on the other hand, are specifically designed to handle combined radial and axial loads. They can support higher axial loads in one direction, making them ideal for applications where thrust forces are significant.
Speed capabilities also differ between these bearing types. Deep groove ball bearings generally have lower friction and can operate at higher speeds than angular contact bearings of the same size. This makes them suitable for applications requiring high rotational speeds with primarily radial loads. Angular contact bearings, while capable of high speeds, may have slightly lower speed limits due to their angled design and the heat generated by the axial load component.
Mounting arrangements are another area of difference. Deep groove ball bearings are typically used in simpler mounting configurations, often as single bearings or in pairs. Angular contact bearings, however, offer more flexibility in mounting arrangements. They can be used in single, duplex (back-to-back or face-to-face), or tandem configurations, allowing for customization based on specific load and stiffness requirements.
Precision and stiffness characteristics also vary between these bearing types. Angular contact bearings generally offer higher precision and stiffness, especially when preloaded. This makes them ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and rigidity, such as machine tool spindles. Deep groove bearings, while precise, may not achieve the same level of stiffness and accuracy in high-precision applications.
Lubrication requirements can also differ. Deep groove bearings typically have simpler lubrication needs and can often operate with grease lubrication for extended periods. Angular contact bearings, especially in high-speed or high-load applications, may require more sophisticated lubrication systems, such as oil circulation or oil-air mist lubrication.
Cost and availability are practical considerations when choosing between these bearing types. Deep groove ball bearings are generally more common and less expensive due to their simpler design and wider range of applications. Angular contact bearings, being more specialized, may be more costly and have longer lead times for certain configurations.
In summary, while both deep groove and angular contact ball bearings are versatile components, their distinct characteristics make them suitable for different applications. Deep groove bearings excel in applications with primarily radial loads and high-speed requirements, while angular contact bearings are better suited for combined load applications requiring high precision and stiffness.
Luoyang Huigong Bearing Technology Co., Ltd. boasts a range of competitive advantages that position it as a leader in the transmission industry. Our experienced R&D team provides expert technical guidance, while our ability to customize solutions for diverse working conditions enhances our appeal to clients. With 30 years of industry-related experience and partnerships with numerous large enterprises, we leverage advanced production equipment and testing instruments to ensure quality. Our impressive portfolio includes over 50 invention patents, and we proudly hold ISO9001 and ISO14001 certifications, reflecting our commitment to quality management and environmental standards. Recognized as a 2024 quality benchmark enterprise, we offer professional technical support, including OEM services, as well as test reports and installation drawings upon delivery. Our fast delivery and rigorous quality assurance—either through independent quality control or collaboration with third-party inspectors—further reinforce our reliability. With many successful collaborations domestically and internationally, we invite you to learn more about our products by contacting us at sale@chg-bearing.com or calling our hotline at +86-0379-65793878.
References
1. SKF Group. (2024). Angular contact ball bearings. SKF.com.
2. NSK Ltd. (2024). Angular Contact Ball Bearings. NSK.com. R
3. Schaeffler Technologies AG & Co. KG. (2024). Angular contact ball bearings. Schaeffler.com.
4. NTN Corporation. (2024). Angular Contact Ball Bearings. NTN.com.
5. Timken Company. (2024). Angular Contact Ball Bearings. Timken.com.
6. American Bearing Manufacturers Association. (2024). Bearing Types. ABMA.com.
7. Machine Design. (2023). Understanding Ball Bearings. MachineDesign.com.
8. Engineering360. (2024). Angular Contact Ball Bearings Information. GlobalSpec.com.
9. Bearing Tips. (2024). What are angular contact bearings? BearingTips.com.
10. RBC Bearings. (2024). Angular Contact Ball Bearings. RBCBearings.com.

